Lasso and elastic net (L1 and L2 penalisation) implemented using a coordinate descent.
The coefficients can be forced to be positive.
Out:
Computing regularization path using the lasso... Computing regularization path using the positive lasso... Computing regularization path using the elastic net... Computing regularization path using the positive elastic net...
print(__doc__)
# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# License: BSD 3 clause
from itertools import cycle
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import lasso_path, enet_path
from sklearn import datasets
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
X = diabetes.data
y = diabetes.target
X /= X.std(axis=0) # Standardize data (easier to set the l1_ratio parameter)
# Compute paths
eps = 5e-3 # the smaller it is the longer is the path
print("Computing regularization path using the lasso...")
alphas_lasso, coefs_lasso, _ = lasso_path(X, y, eps, fit_intercept=False)
print("Computing regularization path using the positive lasso...")
alphas_positive_lasso, coefs_positive_lasso, _ = lasso_path(
X, y, eps, positive=True, fit_intercept=False)
print("Computing regularization path using the elastic net...")
alphas_enet, coefs_enet, _ = enet_path(
X, y, eps=eps, l1_ratio=0.8, fit_intercept=False)
print("Computing regularization path using the positive elastic net...")
alphas_positive_enet, coefs_positive_enet, _ = enet_path(
X, y, eps=eps, l1_ratio=0.8, positive=True, fit_intercept=False)
# Display results
plt.figure(1)
ax = plt.gca()
colors = cycle(['b', 'r', 'g', 'c', 'k'])
neg_log_alphas_lasso = -np.log10(alphas_lasso)
neg_log_alphas_enet = -np.log10(alphas_enet)
for coef_l, coef_e, c in zip(coefs_lasso, coefs_enet, colors):
l1 = plt.plot(neg_log_alphas_lasso, coef_l, c=c)
l2 = plt.plot(neg_log_alphas_enet, coef_e, linestyle='--', c=c)
plt.xlabel('-Log(alpha)')
plt.ylabel('coefficients')
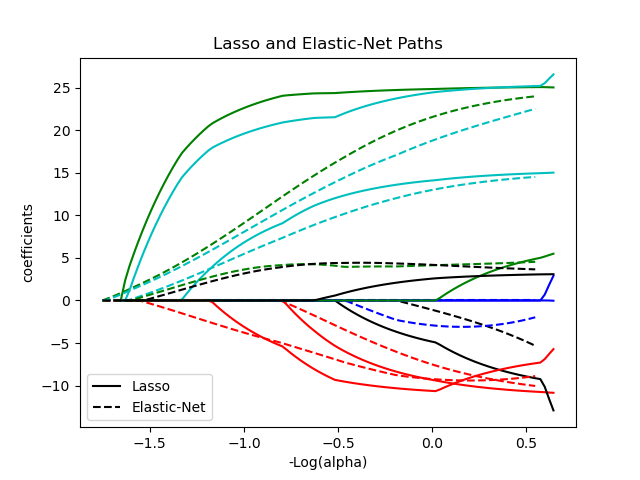
plt.title('Lasso and Elastic-Net Paths')
plt.legend((l1[-1], l2[-1]), ('Lasso', 'Elastic-Net'), loc='lower left')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.figure(2)
ax = plt.gca()
neg_log_alphas_positive_lasso = -np.log10(alphas_positive_lasso)
for coef_l, coef_pl, c in zip(coefs_lasso, coefs_positive_lasso, colors):
l1 = plt.plot(neg_log_alphas_lasso, coef_l, c=c)
l2 = plt.plot(neg_log_alphas_positive_lasso, coef_pl, linestyle='--', c=c)
plt.xlabel('-Log(alpha)')
plt.ylabel('coefficients')
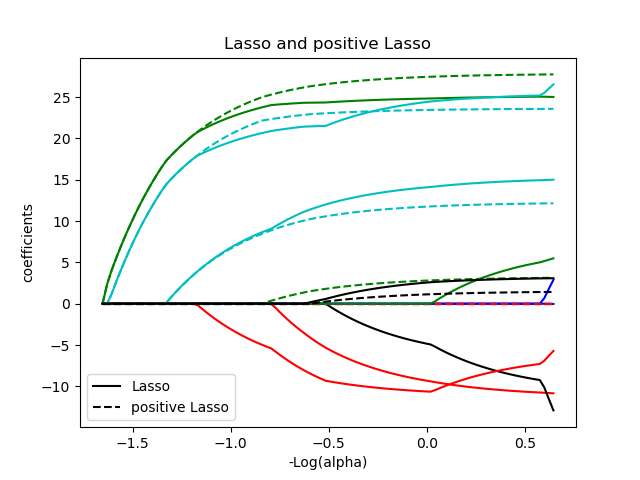
plt.title('Lasso and positive Lasso')
plt.legend((l1[-1], l2[-1]), ('Lasso', 'positive Lasso'), loc='lower left')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.figure(3)
ax = plt.gca()
neg_log_alphas_positive_enet = -np.log10(alphas_positive_enet)
for (coef_e, coef_pe, c) in zip(coefs_enet, coefs_positive_enet, colors):
l1 = plt.plot(neg_log_alphas_enet, coef_e, c=c)
l2 = plt.plot(neg_log_alphas_positive_enet, coef_pe, linestyle='--', c=c)
plt.xlabel('-Log(alpha)')
plt.ylabel('coefficients')
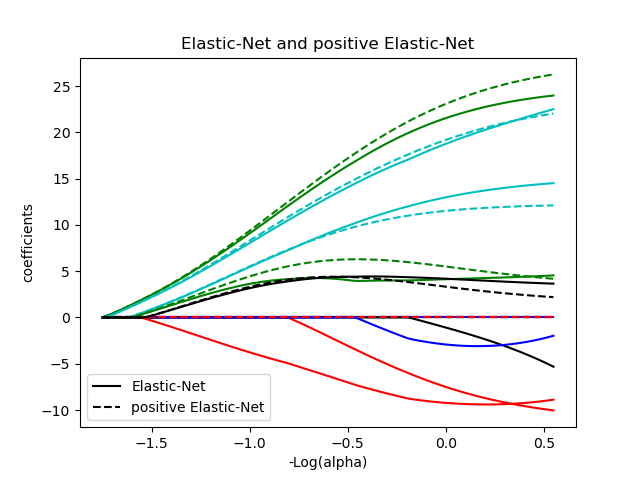
plt.title('Elastic-Net and positive Elastic-Net')
plt.legend((l1[-1], l2[-1]), ('Elastic-Net', 'positive Elastic-Net'),
loc='lower left')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.408 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_lasso_coordinate_descent_path.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_lasso_coordinate_descent_path.ipynb
Please login to continue.