The top and bottom padding and border are always included in the .outerHeight() calculation; if the includeMargin argument is set to true, the margin (top and bottom) is also included.
This method is not applicable to window and document objects; for these, use .height() instead.
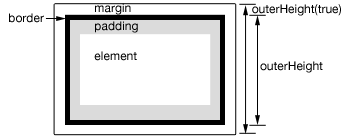 figure 1
figure 1
- The number returned by dimensions-related APIs, including
.outerHeight(), may be fractional in some cases. Code should not assume it is an integer. Also, dimensions may be incorrect when the page is zoomed by the user; browsers do not expose an API to detect this condition. - The value reported by
.outerHeight()is not guaranteed to be accurate when the element or its parent is hidden. To get an accurate value, ensure the element is visible before using.outerHeight(). jQuery will attempt to temporarily show and then re-hide an element in order to measure its dimensions, but this is unreliable and (even when accurate) can significantly impact page performance. This show-and-rehide measurement feature may be removed in a future version of jQuery.
A Boolean indicating whether to include the element's margin in the calculation.
Get the outerHeight of a paragraph.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>outerHeight demo</title>
<style>
p {
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
border: 2px solid #666;
}
</style>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello</p><p></p>
<script>
var p = $( "p:first" );
$( "p:last" ).text(
"outerHeight:" + p.outerHeight() +
" , outerHeight( true ):" + p.outerHeight( true ) );
</script>
</body>
</html>
When calling .outerHeight(value), the value can be either a string (number and unit) or a number. If only a number is provided for the value, jQuery assumes a pixel unit. If a string is provided, however, any valid CSS measurement may be used (such as 100px, 50%, or auto).
A number representing the number of pixels, or a number along with an optional unit of measure appended (as a string).
A function returning the outer height to set. Receives the index position of the element in the set and the old outer height as arguments. Within the function, this refers to the current element in the set.
Change the outer height of each div the first time it is clicked (and change its color).
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>outerHeight demo</title>
<style>
div {
width: 50px;
padding: 10px;
height: 60px;
float: left;
margin: 5px;
background: red;
cursor: pointer;
}
.mod {
background: blue;
cursor: default;
}
</style>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div>d</div>
<div>d</div>
<div>d</div>
<div>d</div>
<div>d</div>
<script>
var modHeight = 60;
$( "div" ).one( "click", function() {
$( this ).outerHeight( modHeight ).addClass( "mod" );
modHeight -= 8;
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Please login to continue.