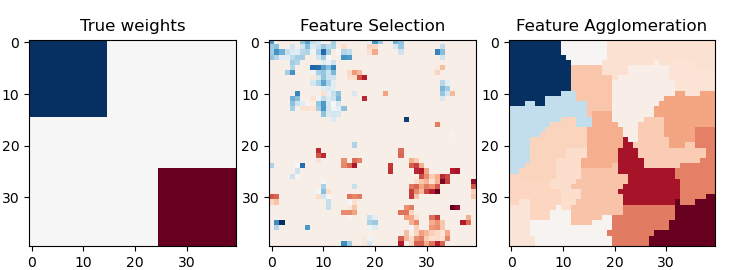
This example compares 2 dimensionality reduction strategies:
- univariate feature selection with Anova
- feature agglomeration with Ward hierarchical clustering
Both methods are compared in a regression problem using a BayesianRidge as supervised estimator.
# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr> # License: BSD 3 clause print(__doc__) import shutil import tempfile import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import linalg, ndimage from sklearn.feature_extraction.image import grid_to_graph from sklearn import feature_selection from sklearn.cluster import FeatureAgglomeration from sklearn.linear_model import BayesianRidge from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline from sklearn.externals.joblib import Memory from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
Generate data
n_samples = 200
size = 40 # image size
roi_size = 15
snr = 5.
np.random.seed(0)
mask = np.ones([size, size], dtype=np.bool)
coef = np.zeros((size, size))
coef[0:roi_size, 0:roi_size] = -1.
coef[-roi_size:, -roi_size:] = 1.
X = np.random.randn(n_samples, size ** 2)
for x in X: # smooth data
x[:] = ndimage.gaussian_filter(x.reshape(size, size), sigma=1.0).ravel()
X -= X.mean(axis=0)
X /= X.std(axis=0)
y = np.dot(X, coef.ravel())
noise = np.random.randn(y.shape[0])
noise_coef = (linalg.norm(y, 2) / np.exp(snr / 20.)) / linalg.norm(noise, 2)
y += noise_coef * noise # add noise
Compute the coefs of a Bayesian Ridge with GridSearch
cv = KFold(2) # cross-validation generator for model selection
ridge = BayesianRidge()
cachedir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
mem = Memory(cachedir=cachedir, verbose=1)
# Ward agglomeration followed by BayesianRidge
connectivity = grid_to_graph(n_x=size, n_y=size)
ward = FeatureAgglomeration(n_clusters=10, connectivity=connectivity,
memory=mem)
clf = Pipeline([('ward', ward), ('ridge', ridge)])
# Select the optimal number of parcels with grid search
clf = GridSearchCV(clf, {'ward__n_clusters': [10, 20, 30]}, n_jobs=1, cv=cv)
clf.fit(X, y) # set the best parameters
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[-1][1].coef_
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[0][1].inverse_transform(coef_)
coef_agglomeration_ = coef_.reshape(size, size)
# Anova univariate feature selection followed by BayesianRidge
f_regression = mem.cache(feature_selection.f_regression) # caching function
anova = feature_selection.SelectPercentile(f_regression)
clf = Pipeline([('anova', anova), ('ridge', ridge)])
# Select the optimal percentage of features with grid search
clf = GridSearchCV(clf, {'anova__percentile': [5, 10, 20]}, cv=cv)
clf.fit(X, y) # set the best parameters
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[-1][1].coef_
coef_ = clf.best_estimator_.steps[0][1].inverse_transform(coef_.reshape(1, -1))
coef_selection_ = coef_.reshape(size, size)
Out:
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.cluster.hierarchical.ward_tree...
ward_tree(array([[-0.451933, ..., -0.675318],
...,
[ 0.275706, ..., -1.085711]]),
<1600x1600 sparse matrix of type '<type 'numpy.int64'>'
with 7840 stored elements in COOrdinate format>, n_clusters=None)
________________________________________________________ward_tree - 0.2s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.cluster.hierarchical.ward_tree...
ward_tree(array([[ 0.905206, ..., 0.161245],
...,
[-0.849835, ..., -1.091621]]),
<1600x1600 sparse matrix of type '<type 'numpy.int64'>'
with 7840 stored elements in COOrdinate format>, n_clusters=None)
________________________________________________________ward_tree - 0.2s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.cluster.hierarchical.ward_tree...
ward_tree(array([[ 0.905206, ..., -0.675318],
...,
[-0.849835, ..., -1.085711]]),
<1600x1600 sparse matrix of type '<type 'numpy.int64'>'
with 7840 stored elements in COOrdinate format>, n_clusters=None)
________________________________________________________ward_tree - 0.2s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.feature_selection.univariate_selection.f_regression...
f_regression(array([[-0.451933, ..., 0.275706],
...,
[-0.675318, ..., -1.085711]]),
array([ 25.267703, ..., -25.026711]))
_____________________________________________________f_regression - 0.0s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.feature_selection.univariate_selection.f_regression...
f_regression(array([[ 0.905206, ..., -0.849835],
...,
[ 0.161245, ..., -1.091621]]),
array([ -27.447268, ..., -112.638768]))
_____________________________________________________f_regression - 0.0s, 0.0min
________________________________________________________________________________
[Memory] Calling sklearn.feature_selection.univariate_selection.f_regression...
f_regression(array([[ 0.905206, ..., -0.849835],
...,
[-0.675318, ..., -1.085711]]),
array([-27.447268, ..., -25.026711]))
_____________________________________________________f_regression - 0.0s, 0.0min
Inverse the transformation to plot the results on an image
plt.close('all')
plt.figure(figsize=(7.3, 2.7))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(coef, interpolation="nearest", cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
plt.title("True weights")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(coef_selection_, interpolation="nearest", cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
plt.title("Feature Selection")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(coef_agglomeration_, interpolation="nearest", cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
plt.title("Feature Agglomeration")
plt.subplots_adjust(0.04, 0.0, 0.98, 0.94, 0.16, 0.26)
plt.show()
# Attempt to remove the temporary cachedir, but don't worry if it fails
shutil.rmtree(cachedir, ignore_errors=True)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.336 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_feature_agglomeration_vs_univariate_selection.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_feature_agglomeration_vs_univariate_selection.ipynb
Please login to continue.