Demonstrate Gradient Boosting on the Boston housing dataset.
This example fits a Gradient Boosting model with least squares loss and 500 regression trees of depth 4.
print(__doc__) # Author: Peter Prettenhofer <peter.prettenhofer@gmail.com> # # License: BSD 3 clause import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import ensemble from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.utils import shuffle from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
Load data
boston = datasets.load_boston() X, y = shuffle(boston.data, boston.target, random_state=13) X = X.astype(np.float32) offset = int(X.shape[0] * 0.9) X_train, y_train = X[:offset], y[:offset] X_test, y_test = X[offset:], y[offset:]
Fit regression model
params = {'n_estimators': 500, 'max_depth': 4, 'min_samples_split': 2,
'learning_rate': 0.01, 'loss': 'ls'}
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(**params)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, clf.predict(X_test))
print("MSE: %.4f" % mse)
Out:
MSE: 6.6213
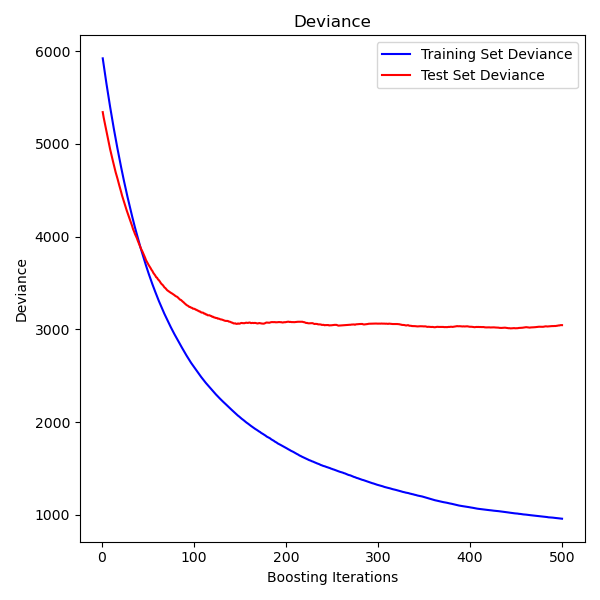
Plot training deviance
# compute test set deviance
test_score = np.zeros((params['n_estimators'],), dtype=np.float64)
for i, y_pred in enumerate(clf.staged_predict(X_test)):
test_score[i] = clf.loss_(y_test, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.title('Deviance')
plt.plot(np.arange(params['n_estimators']) + 1, clf.train_score_, 'b-',
label='Training Set Deviance')
plt.plot(np.arange(params['n_estimators']) + 1, test_score, 'r-',
label='Test Set Deviance')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlabel('Boosting Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Deviance')
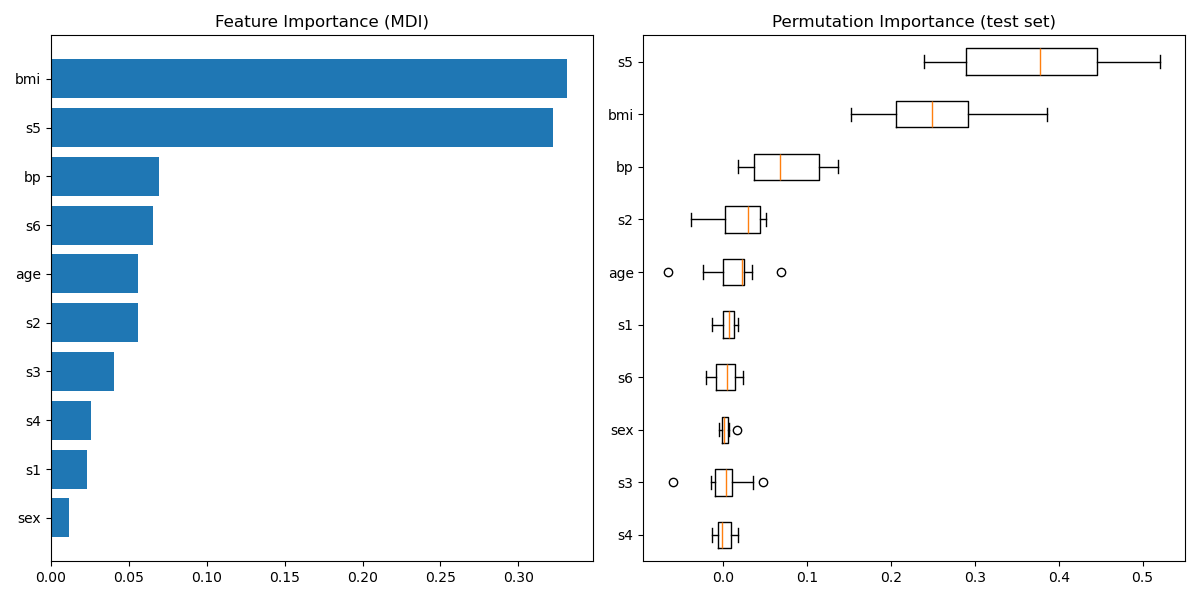
Plot feature importance
feature_importance = clf.feature_importances_
# make importances relative to max importance
feature_importance = 100.0 * (feature_importance / feature_importance.max())
sorted_idx = np.argsort(feature_importance)
pos = np.arange(sorted_idx.shape[0]) + .5
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.barh(pos, feature_importance[sorted_idx], align='center')
plt.yticks(pos, boston.feature_names[sorted_idx])
plt.xlabel('Relative Importance')
plt.title('Variable Importance')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.548 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_gradient_boosting_regression.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_gradient_boosting_regression.ipynb
Please login to continue.