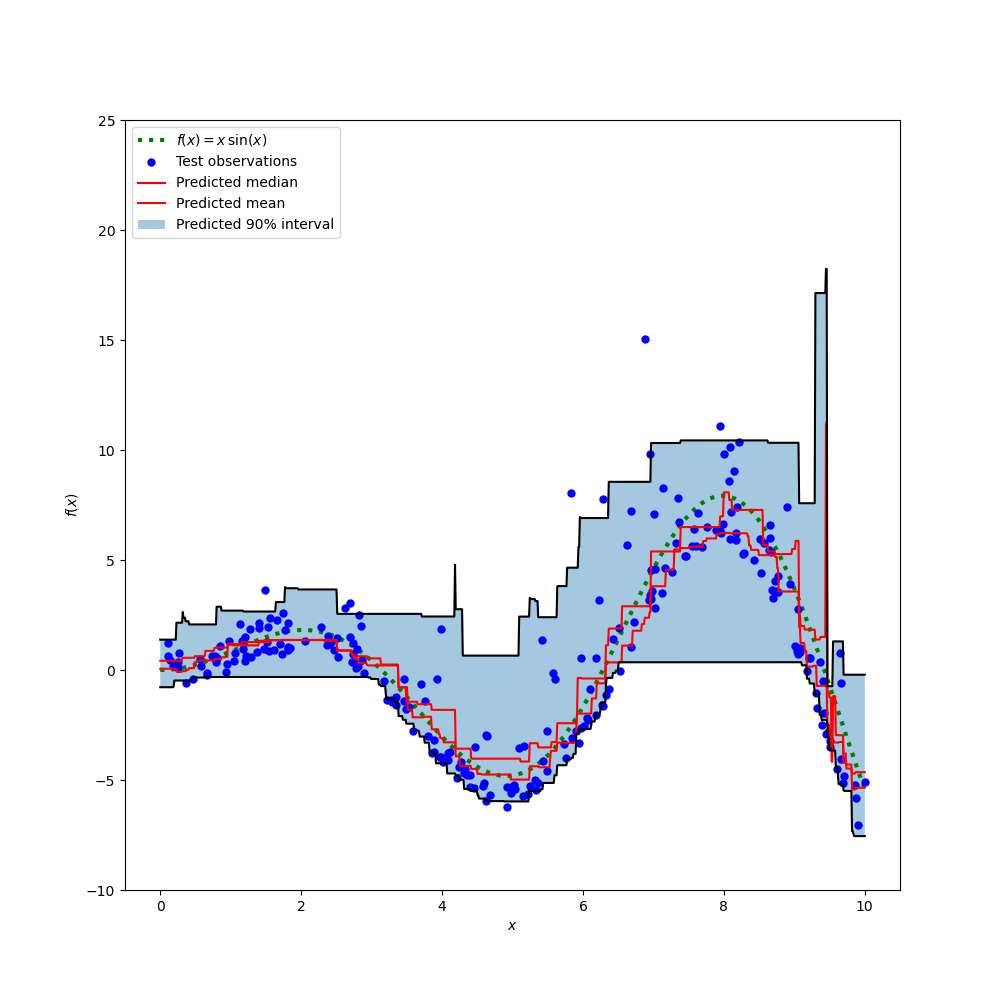
This example shows how quantile regression can be used to create prediction intervals.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
np.random.seed(1)
def f(x):
"""The function to predict."""
return x * np.sin(x)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# First the noiseless case
X = np.atleast_2d(np.random.uniform(0, 10.0, size=100)).T
X = X.astype(np.float32)
# Observations
y = f(X).ravel()
dy = 1.5 + 1.0 * np.random.random(y.shape)
noise = np.random.normal(0, dy)
y += noise
y = y.astype(np.float32)
# Mesh the input space for evaluations of the real function, the prediction and
# its MSE
xx = np.atleast_2d(np.linspace(0, 10, 1000)).T
xx = xx.astype(np.float32)
alpha = 0.95
clf = GradientBoostingRegressor(loss='quantile', alpha=alpha,
n_estimators=250, max_depth=3,
learning_rate=.1, min_samples_leaf=9,
min_samples_split=9)
clf.fit(X, y)
# Make the prediction on the meshed x-axis
y_upper = clf.predict(xx)
clf.set_params(alpha=1.0 - alpha)
clf.fit(X, y)
# Make the prediction on the meshed x-axis
y_lower = clf.predict(xx)
clf.set_params(loss='ls')
clf.fit(X, y)
# Make the prediction on the meshed x-axis
y_pred = clf.predict(xx)
# Plot the function, the prediction and the 90% confidence interval based on
# the MSE
fig = plt.figure()
plt.plot(xx, f(xx), 'g:', label=u'$f(x) = x\,\sin(x)$')
plt.plot(X, y, 'b.', markersize=10, label=u'Observations')
plt.plot(xx, y_pred, 'r-', label=u'Prediction')
plt.plot(xx, y_upper, 'k-')
plt.plot(xx, y_lower, 'k-')
plt.fill(np.concatenate([xx, xx[::-1]]),
np.concatenate([y_upper, y_lower[::-1]]),
alpha=.5, fc='b', ec='None', label='90% prediction interval')
plt.xlabel('$x$')
plt.ylabel('$f(x)$')
plt.ylim(-10, 20)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.311 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_gradient_boosting_quantile.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_gradient_boosting_quantile.ipynb
Please login to continue.