This example shows how to perform univariate feature selection before running a SVC (support vector classifier) to improve the classification scores.
print(__doc__) import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import svm, datasets, feature_selection from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
Import some data to play with
digits = datasets.load_digits() y = digits.target # Throw away data, to be in the curse of dimension settings y = y[:200] X = digits.data[:200] n_samples = len(y) X = X.reshape((n_samples, -1)) # add 200 non-informative features X = np.hstack((X, 2 * np.random.random((n_samples, 200))))
Create a feature-selection transform and an instance of SVM that we combine together to have an full-blown estimator
transform = feature_selection.SelectPercentile(feature_selection.f_classif)
clf = Pipeline([('anova', transform), ('svc', svm.SVC(C=1.0))])
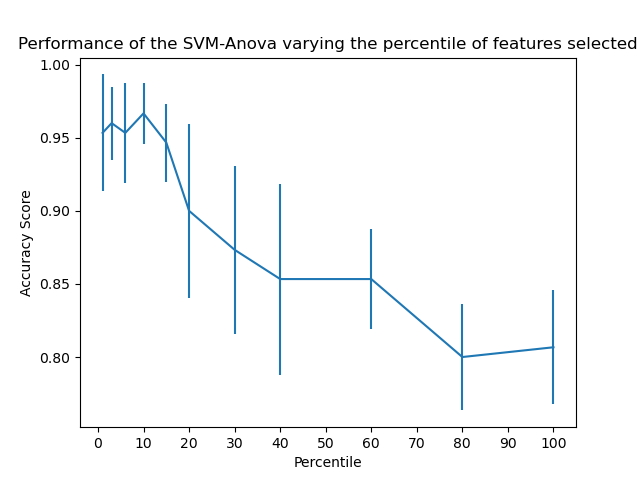
Plot the cross-validation score as a function of percentile of features
score_means = list()
score_stds = list()
percentiles = (1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 60, 80, 100)
for percentile in percentiles:
clf.set_params(anova__percentile=percentile)
# Compute cross-validation score using 1 CPU
this_scores = cross_val_score(clf, X, y, n_jobs=1)
score_means.append(this_scores.mean())
score_stds.append(this_scores.std())
plt.errorbar(percentiles, score_means, np.array(score_stds))
plt.title(
'Performance of the SVM-Anova varying the percentile of features selected')
plt.xlabel('Percentile')
plt.ylabel('Prediction rate')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.620 seconds)
Download Python source code:
plot_svm_anova.py
Download IPython notebook:
plot_svm_anova.ipynb
Please login to continue.