-
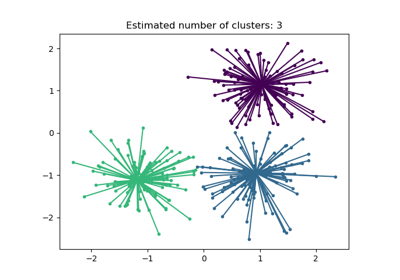
sklearn.datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=100, n_features=2, centers=3, cluster_std=1.0, center_box=(-10.0, 10.0), shuffle=True, random_state=None)[source] -
Generate isotropic Gaussian blobs for clustering.
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: n_samples : int, optional (default=100)
The total number of points equally divided among clusters.
n_features : int, optional (default=2)
The number of features for each sample.
centers : int or array of shape [n_centers, n_features], optional
(default=3) The number of centers to generate, or the fixed center locations.
cluster_std : float or sequence of floats, optional (default=1.0)
The standard deviation of the clusters.
center_box : pair of floats (min, max), optional (default=(-10.0, 10.0))
The bounding box for each cluster center when centers are generated at random.
shuffle : boolean, optional (default=True)
Shuffle the samples.
random_state : int, RandomState instance or None, optional (default=None)
If int, random_state is the seed used by the random number generator; If RandomState instance, random_state is the random number generator; If None, the random number generator is the RandomState instance used by
np.random.Returns: X : array of shape [n_samples, n_features]
The generated samples.
y : array of shape [n_samples]
The integer labels for cluster membership of each sample.
See also
-
make_classification - a more intricate variant
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs >>> X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=10, centers=3, n_features=2, ... random_state=0) >>> print(X.shape) (10, 2) >>> y array([0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 0])
-
sklearn.datasets.make_blobs()
Examples using
2025-01-10 15:47:30


Please login to continue.